"Foil leather" typically refers to a type of leather that has undergone a foil treatment to achieve a metallic or reflective appearance. This process involves applying a metallic foil or film onto the surface of the leather, resulting in a shiny and eye-catching finish. Foil leather is often used in fashion and accessories to create a distinctive and glamorous look. Here's more information about foil leather:
Features of Foil Leather:
Appearance:
- Foil leather is known for its metallic or reflective appearance, resembling the look of precious metals like gold or silver.
Variety of Colors:
- While gold and silver are popular choices, foil leather comes in various colors, offering versatility in design.
Texture:
- The foil treatment does not significantly alter the natural texture of the leather. Depending on the process, it can have a smooth or slightly textured surface.
Uses and Applications:
Fashion Accessories:
- Foil leather is commonly used in the production of fashion accessories such as handbags, wallets, belts, and shoes to add a touch of glamour.
Apparel:
- Some clothing items, especially in the fashion industry, may incorporate foil leather for unique and stylish designs.
Home Decor:
- Foil leather is occasionally used in home decor items like upholstery, throw pillows, or decorative accents.
Care and Maintenance:
Cleaning:
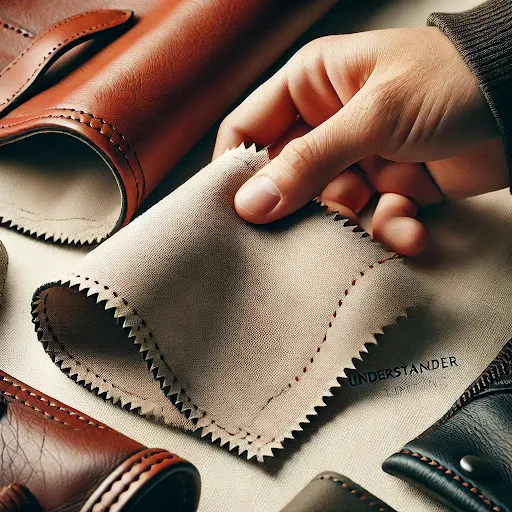
- Foil leather should be cleaned with care using a soft, damp cloth. Avoid using abrasive cleaners that could damage the foil treatment.
Avoid Scratching:
- Like any leather product, foil leather can be susceptible to scratches. Avoid sharp objects and rough surfaces to maintain its appearance.
Fashion Trends:
Seasonal Trends:
- Foil leather often follows seasonal fashion trends. It may be more popular during certain seasons or for specific occasions.
High Fashion:
- High-end fashion designers may use foil leather to create statement pieces that stand out on the runway.
Availability:
Market Presence:
- Foil leather products can be found in fashion boutiques, department stores, and online retailers specializing in leather goods.
Customization:
- Some manufacturers may offer customization options, allowing customers to choose the color and finish of the foil treatment.
Sustainability Considerations:
- Material Source:
- The sustainability of foil leather depends on the sourcing of the base leather and the environmental practices of the manufacturing process.